Jump to final component.
Dynamic loading of message catalogs¶
I18nProvider doesn’t assume anything about your app and it’s your
responsibility to load messages based on active language. Here’s an example of
I18nLoader component which is connected to Redux store and loads message
catalogs using dynamic import in Webpack.
Setup¶
Warning
You don’t have to install following Babel plugins if you’re using Create React App or similar framework which already has it.
We are using the Dynamic Import() Proposal
to ECMAScript. We need to install babel-plugin-syntax-dynamic-import and
babel-plugin-dynamic-import-node to make it work. Also, the code examples given here make use of babel-plugin-transform-class-properties
yarn add --dev babel-plugin-syntax-dynamic-import babel-plugin-dynamic-import-node babel-plugin-transform-class-properties
Warning
babel-plugin-dynamic-import-node is required when running tests in Jest.
// .babelrc
{
"plugins": [
"syntax-dynamic-import",
"transform-class-properties"
],
"env": {
"test": {
"plugins": [
"dynamic-import-node"
]
}
}
Component¶
Let’s start with the component. We’re going to wrap <I18nProvider>
from @lingui/react. Active language is loaded from redux store, while
messages are dynamically loaded and stored in local state.
The render() method looks like this:
render () {
const { children, language } = this.props
const { catalogs } = this.state
// Skip rendering when catalog isn't loaded.
if (!catalogs[language]) return
return (
<I18nProvider language={language} catalogs={catalogs}>
{children}
</I18nProvider>
)
}
Next, we need to load message catalog when language changes which isn’t done yet. Dynamic import returns a promise and we don’t want to re-render
our component until the message catalog is loaded. Let’s add a
shouldComponentUpdate() method:
shouldComponentUpdate(nextProps, nextState) {
const { language } = nextProps
const { catalogs } = nextState
if (language !== this.props.language && !catalogs[language]) {
// Start loading message catalog and skip update
this.loadCatalog(language)
return false
}
return true
}
shouldComponentUpdate isn’t called during the first render, so we need
trigger loading of catalog manually in componentDidMount:
componentDidMount() {
this.loadCatalog(this.props.language)
}
Loading of message catalogs¶
The most important piece in this story is loadCatalog() method. It’s
necessary to load compiled message catalogs. The recommended way is compile
messages on-the-fly using @lingui/loader, but it’s also possible to load
compiled messages.js directly.
yarn add --dev @lingui/loader
Here we use the dynamic import syntax to load the message catalog:
loadCatalog = async (language) => {
// using @lingui/loader - load raw messages.json
const catalog = await import(
/* webpackMode: "lazy", webpackChunkName: "i18n-[index]" */
`@lingui/loader!locale/${language}/messages.json`)
// load compiled messages.js
// const catalog = await import(
// /* webpackMode: "lazy", webpackChunkName: "i18n-[index]" */
// `locale/${language}/messages.js`)
this.setState(state => ({
catalogs: {
...state.catalogs,
[language]: catalog
}
}))
}
Dynamic import returns a promise, so we can either use async/await keywords or good old promises:
loadCatalog = (language) => {
import(
/* webpackMode: "lazy", webpackChunkName: "i18n-[index]" */
`@lingui/loader!locale/${language}/messages.json`)
.then(catalog =>
this.setState(state => ({
catalogs: {
...state.catalogs,
[language]: catalog
}
}))
)
}
The comment before message catalog path is webpack’s magic comment.
webpackMode: lazy means, that chunks are loaded as requested.
webpackChunkName: "i18n-[index]" overrides default chunk name for this import.
Final component¶
Here’s the full source of I18nLoader component:
import React from 'react'
import { connect } from 'react-redux'
import { I18nProvider } from '@lingui/react'
export class I18nLoader extends React.Component {
state = {
catalogs: {},
}
loadCatalog = async (language) => {
const catalog = await import(
/* webpackMode: "lazy", webpackChunkName: "i18n-[index]" */
`@lingui/loader!locale/${language}/messages.json`)
this.setState(state => ({
catalogs: {
...state.catalogs,
[language]: catalog
}
}))
}
componentDidMount() {
this.loadCatalog(this.props.language)
}
shouldComponentUpdate(nextProps, nextState) {
const { language } = nextProps
const { catalogs } = nextState
if (language !== this.props.language && !catalogs[language]) {
this.loadCatalog(language)
return false
}
return true
}
render () {
const { children, language } = this.props
const { catalogs } = this.state
// Skip rendering when catalog isn't loaded.
if (!catalogs[language]) return
return (
<I18nProvider language={language} catalogs={catalogs}>
{children}
</I18nProvider>
)
}
}
// Example: depends on implementation of reducer
const getLanguage = state => state.locale.language
export default connect(state => ({
language: getLanguage(state)
}))(I18nLoader)
Conclusion¶
Looking at the content of build dir, we see one chunk per language:
i18n-0.c433b3bd.chunk.js
i18n-1.f0cf2e3d.chunk.js
main.ab4626ef.js
When page is loaded initially, only main bundle and bundle for the first language are loaded:
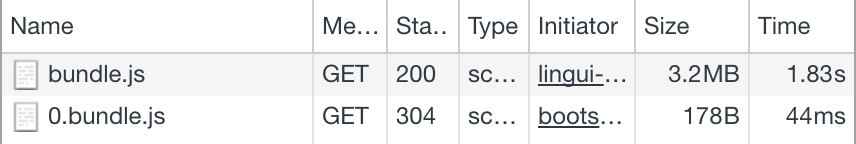
After changing language in UI, the second language bundle is loaded:
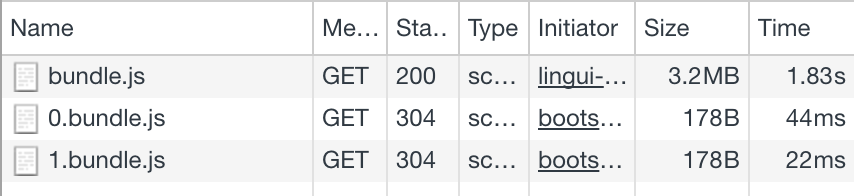
And that’s it! 🎉